Translation Elongation Rates: Insights and Implications
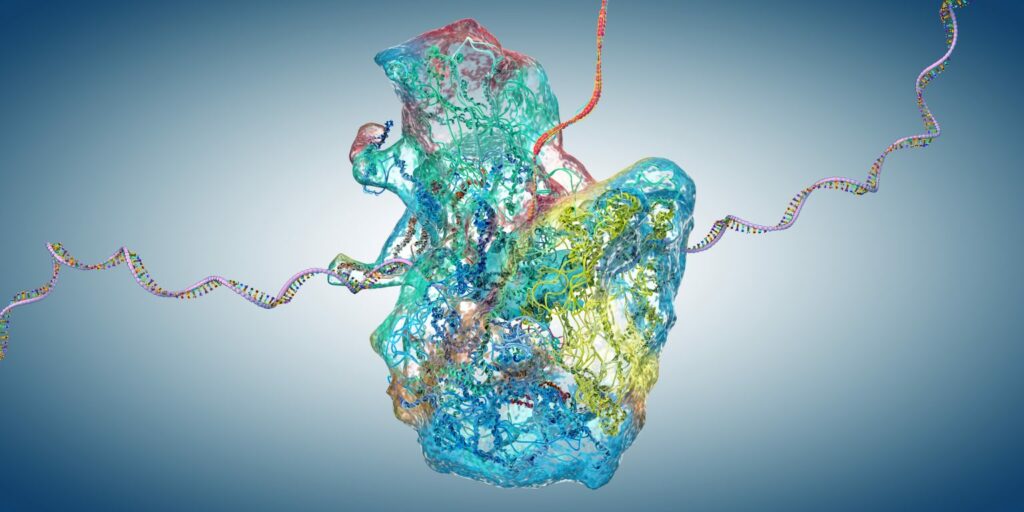
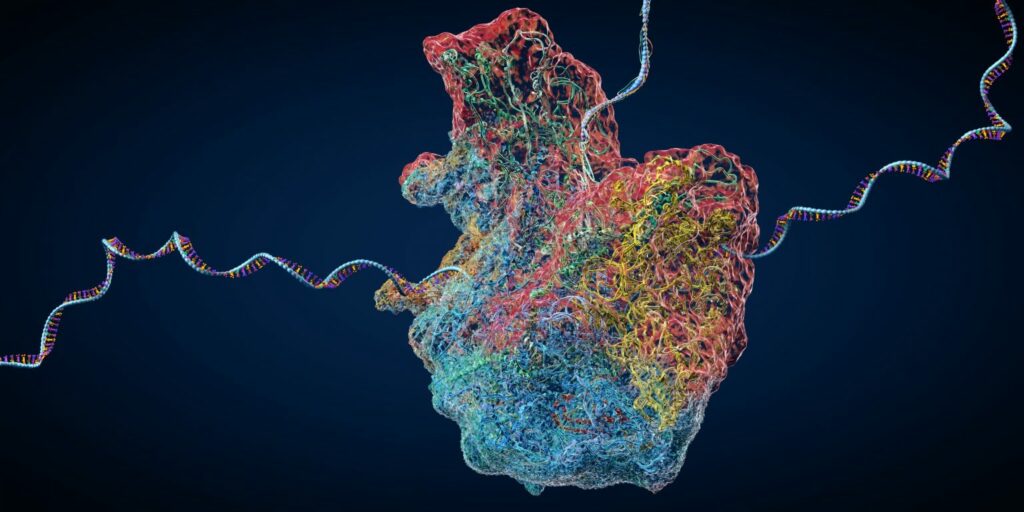
Translation Elongation Rates In order to maintain a healthy proteome, the ribosome must not only generate sequences of peptides in sufficient quantities to serve their biological purpose but must also ensure that these polymers correctly fold into their native structures to yield fully functional proteins. Somewhat counter-intuitively, these mutually beneficial processes of protein synthesis and […]
Translation Elongation Rates: Insights and Implications Read More »